

(ttsz/iStock via Getty Images Plus)ĭNA is found inside the cells of every living thing. Messenger RNA carries genetic information from DNA in the highly protected nucleus out to the rest of the cell, where structures called ribosomes can build proteins according to the DNA blueprint.
#MESSENGER RNA CODE#
It’s the molecule that contains all of your genes spelled out in a four-letter code – A, C, G and T.
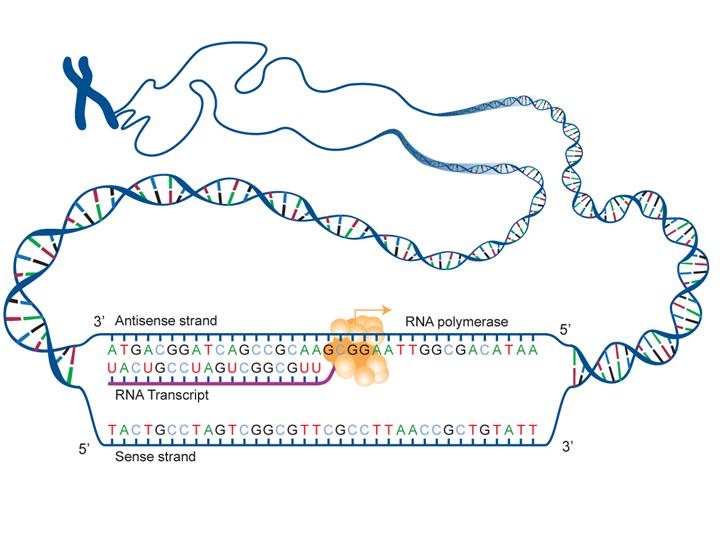
Here’s a crash course in just what mRNA is and the important job it does. Scientists think RNA originated in the earliest life forms, even before DNA existed. It evolved billions of years ago and is naturally found in every cell in your body. But mRNA itself is not a new invention from the lab. It’s the key ingredient in the Pfizer and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines. doi: 10.1002/wrna.One surprising star of the coronavirus pandemic response has been the molecule called mRNA. This article surveys the design, mode of action, and capabilities of state-of-the-art mRNA vaccines, focusing on the paradigm of influenza prophylaxis. Messenger RNA vaccines induce balanced immune responses including B cells, helper T cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, rendering them an extremely adaptable platform. The formation of native antigen in situ affords great versatility, including intracellular localization, membrane association, posttranslational modification, supra-molecular assembly, or targeted structural optimization of delivered antigen. (3) RNA can be tailored to provide potent adjuvant stimuli to the innate immune system by direct activation of RNA-specific receptors this may reduce the need for additional adjuvants. This greatly reduces general complications associated with biological vaccine production, such as handling of infectious agents, genetic variability, environmental risks, or restrictions to vaccine distribution. (2) mRNA vaccines are synthetically produced by an enzymatic process, just requiring information about the nucleic acid sequence of the desired antigen. These characteristics also guarantee tight control over their immunogenic profile (including avoidance of vector-specific immune responses that could interfere with repeated administration), pharmacokinetics, and dosing. In the environment and upon physical contact, RNA is rapidly degraded by ubiquitous RNases and cannot persist. At the conceptual level, mRNA-based vaccines-more than other genetic vectors-combine the simplicity, safety, and focused immunogenicity of subunit vaccines with favorable immunological properties of live viral vaccines: (1) mRNA vaccines are molecularly defined and carry no excess information. These data indicate wider applicability to infectious disease and should encourage continued translation of mRNA-based prophylactic vaccines into human clinical trials. Twenty years after the demonstration that messenger RNA (mRNA) was expressed and immunogenic upon direct injection in mice, the first successful proof-of-concept of specific protection against viral infection in small and large animals was reported.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
